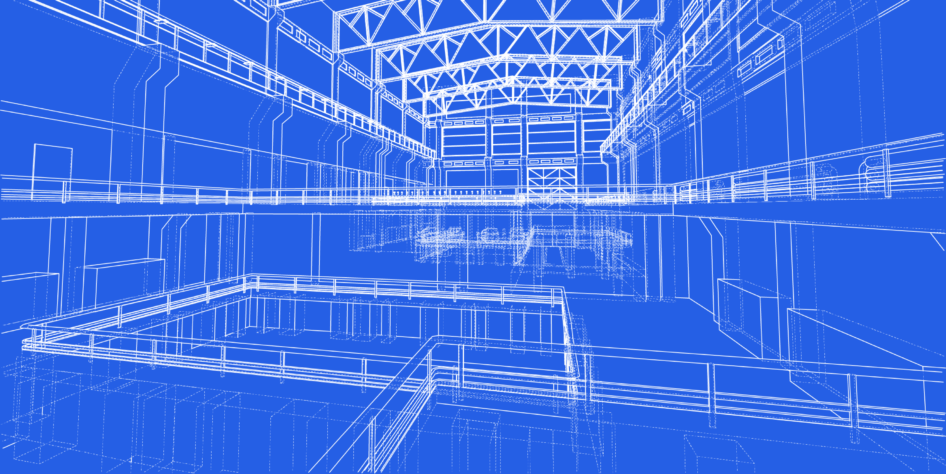
Building Information Modelling (BIM)
BIM offers a streamlined and simplified approach to designing, constructing and maintaining buildings. Using a system of 3D modelling, along with assigned metadata containing information on construction materials, costs, services etc., our building information modelling services create a common baseline for any work required on a site throughout its lifetime.
Having a single, accurate, digital reference point for all contractors, from surveyors and builders to architects and project managers, simplifies processes and saves time. If required on a project, traditional drawings can be produced as a 2D projection of the 3D model. BIM is now a requirement for all UK Government contracts and is fast becoming the industry standard. Our extensive use of 3D CAD and laser scanning makes us a qualified partner for your BIM requirements.
Laser scanning and 3D modelling
Laser scanning provides highly accurate, three-dimensional images enabling designers to experience and work directly with real-world conditions by viewing and manipulating rich point-clouds.
We are highly skilled in the use of a large range of 3D scanners and choose equipment carefully depending on the task in hand and the accuracy required. The data collected can be delivered as a point cloud, in 2D or 3D BIM compatible formats and/or a fully developed model in Revit or AECOsim.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 3d building information modelling (BIM)?
BIM is a digital process used in the architecture, engineering, and construction industries to design, build, and manage buildings and infrastructure projects. At the heart of a BIM project is a 3D model (or ‘digital twin’) that represents the physical structure of the building or infrastructure. This model includes detailed information about the building’s components (walls, doors, windows, electrical systems, plumbing, etc.) and their relationships to one another.
What are the benefits of 3d building information modelling (BIM)?
- Clearer Visualisation: 3D BIM allows clients to see a project before it’s built. This improves understanding of how the end result will look and function, improving design-stage decision-making.
- Cost Prediction and Control: BIM can provide accurate cost estimates and allow for better budget control throughout the project. By detecting potential issues early on, clients can avoid costly reworks and delays.
- Facility Management and Maintenance: Post-construction, the 3D BIM model can be used for facility management. Clients can use the data for asset management, maintenance schedules, and future refurbishments.
- Regulatory Compliance: The UK has stringent building regulations (such as those found in the Building Regulations 2010 and planning standards). 3D BIM models can help ensure compliance with these regulations by providing a clear digital record of the design and its adherence to the codes.
- Accurate Documentation: BIM provides comprehensive documentation, which is essential for legal and regulatory purposes. It can also be helpful for future refurbishment projects or for audits.
- Government Initiatives: In the UK, the government has been pushing for the adoption of BIM in public sector projects. The Government Construction Strategy requires Level 2 BIM on all government projects, meaning clients working with public sector organisations will need to incorporate BIM to comply with these mandates.
- Better Access to Funding: Clients may find that adopting BIM helps them secure government or private sector funding, as it demonstrates efficiency, risk management, and a forward-thinking approach.
Examples of 3d building information modelling (BIM) software?
Autodesk Revit
- Overview: One of the most well-known BIM tools, Autodesk Revit is designed for architects, engineers, and contractors. It allows users to design and model in 3D, integrating architectural, structural, and MEP elements in one platform.
- Features: Parametric design, real-time collaboration, clash detection, and extensive library support for materials and components.
Graphisoft ArchiCAD
- Overview: A powerful BIM software for architects, ArchiCAD offers an intuitive 3D design environment. It is known for its ease of use and rich visualisation capabilities.
- Features: Open BIM compatibility, 3D modelling, energy analysis, and easy collaboration between project teams.
Bentley Systems (MicroStation and Open Buildings Designer)
- Overview: MicroStation is a comprehensive design and modelling platform used for large-scale infrastructure projects. Bentley also offers BIM tools for civil, structural, and mechanical disciplines.
- Features: Advanced 3D modelling, multi-discipline collaboration, and integration with other Bentley products for infrastructure management.
How is the industry using 3d building information modelling in construction?
4D BIM (Time Simulation): Contractors use BIM to simulate the construction sequence (time-based modelling), known as 4D BIM. This helps visualize the construction process over time, plan workflows, and optimize construction schedules. It can be used to predict delays and identify potential risks.
Logistics and Site Management: BIM models are used to plan and manage logistics on the construction site, such as equipment placement, material deliveries, and worker safety. Site managers can visualize how the site will evolve throughout the project, enabling better resource allocation and site organization.
Cost Management (5D BIM): 5D BIM incorporates cost data into the 3D model, enabling real-time cost estimation and tracking. This helps manage the budget, control costs, and prevent cost overruns by providing accurate material quantities and labour requirements upfront.
Construction Quality Control: BIM can assist in monitoring construction quality by comparing the actual progress against the model, checking for compliance with specifications, and identifying any deviations early on. This helps reduce errors and ensures that the construction meets the required standards.
What are the different levels of development (LODs)?
LODs, (aka Levels of Development) refer to the degree of detail and reliability in the information included in a BIM model at different stages of a project. The LOD helps define what information is expected and at what level of precision, guiding project teams on how detailed a model should be at each phase.
Common LODs in UK BIM:
- LOD 100 (Conceptual Design): Basic model elements with approximate size and location, used for initial design and feasibility studies.
- LOD 200 (Schematic Design): Elements are represented with approximate quantities, size, and shape. More detailed than LOD 100, it allows for better coordination among disciplines.
- LOD 300 (Design Development): Elements are accurately modelled with precise dimensions, materials, and quantities. This LOD is used for detailed design and construction planning.
- LOD 400 (Construction Documentation): Models are highly detailed, including fabrication and assembly information. This LOD is used for construction and procurement.
- LOD 500 (As-built): The model is fully accurate and reflects the final built condition. It includes all as-built details for operations and facilities management.
Using LODs helps ensure that the appropriate level of detail is available at each project stage, supporting better coordination, accuracy, and decision-making throughout the construction process.












